How to distinguish between a negative pressure weighing hood and a laminar flow hood?
How to distinguish between a negative pressure weighing hood and a laminar flow hood?The laminar flow hood provides a local positive pressure environment and vertical one-way air flow; the weighing hood provides a local negative pressure environment and also a vertical one-way airflow. The laminar flow hood does not have a return air panel, and the purified air is discharged directly into the clean room; the weighing hood has a return air panel, and part of the purified air flows back to the fan box through the return air panel, and a small part is discharged into the clean room for maintenance Negative pressure environment inside the weighing hood. Laminar flow hoods are mainly used to operate non-ferrous materials, easily volatile and easily oxidized materials, and are suitable for chemical, pharmaceutical, food, and other industries.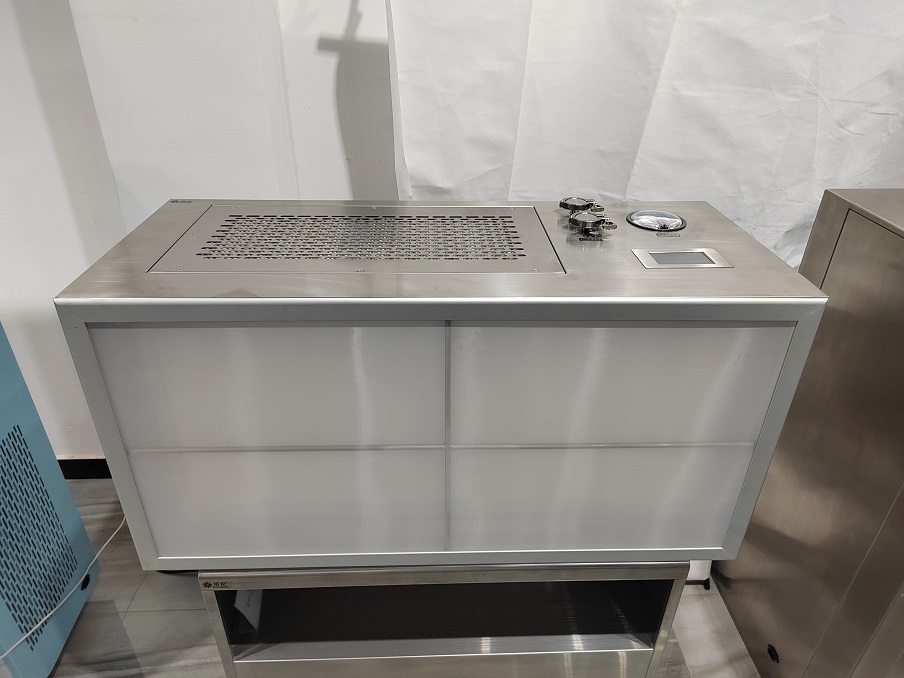 A weighing hood is a kind of protective equipment used for weighing, mixing, coating, and other operations. It is used for weighing and packaging medicines or other products during the production process. It is used alone; a laminar flow hood is used for key processes. The section provides a local clean environment and can be installed above the equipment in the process section that needs to be protected. The principle is to separate the operating area from the inside of the machine through negative pressure to avoid the impact of dust, odor, radioactivity, etc. in the working area on the operator and the surrounding environment. Weighing hoods are used for weighing and packaging of drugs or other products during the production process and are used alone; laminar flow hoods are used to provide a local clean environment for key process sections and can be installed above the equipment in the process sections that need to be protected. , mainly used in biology, chemical industry, medicine, and other industries, suitable for experimental operations such as mixing, coating, and weighing of organic substances.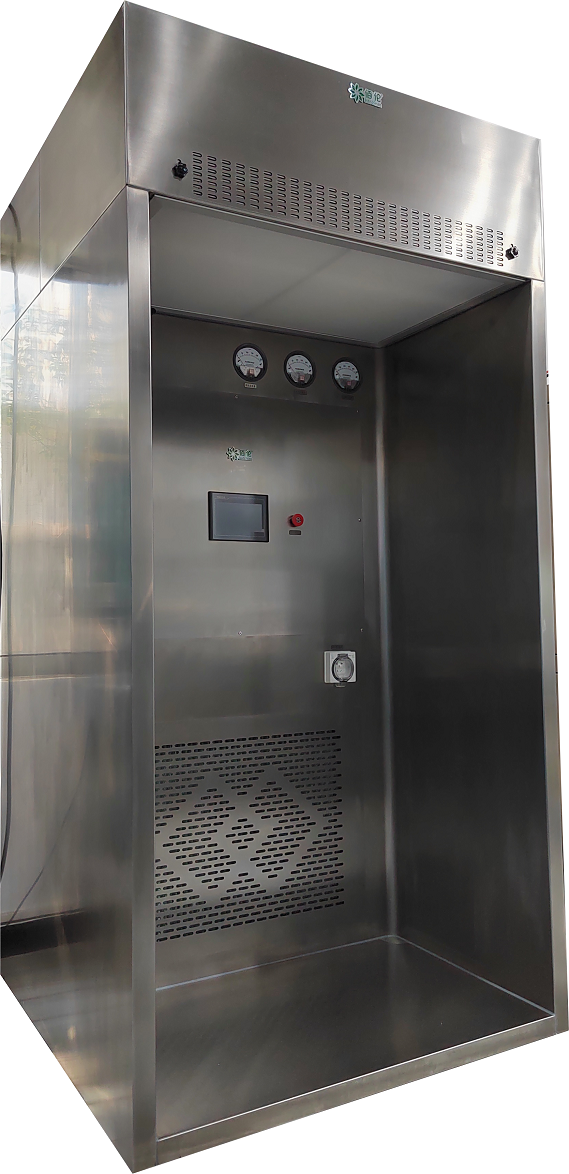  1. Design principles The design principle of the laminar flow hood is to flow the purified air downward through the horizontal air duct through the filter to form a sterile and dust-free positive laminar flow in the work area, thereby ensuring the purification of the operating area. The design principle of the negative pressure weighing cover is to set an air outlet on the top of the pickup cover to force the gas or steam generated in the work area to be discharged, thereby forming a negative pressure area to prevent the release of dust and odor. Laminar flow hood is one of the most commonly used purification equipment in Class A clean areas. The air in the clean room of the laminar flow hood is filtered by the fan through the high-efficiency filter and blown out from the air outlet surface through the flow equalizing film to form a clean vertical unidirectional flow. The clean airflow flows through the work area at a uniform cross-sectional wind speed, thereby removing the air in the clean area. The dust is taken away, forming a Class A clean environment. Taking the pneumonia vaccine workshop of a listed vaccine company as an example, laminar flow hoods are used in the centrifuge room, ultrafiltration room, sedimentation room, and extraction and sedimentation room. 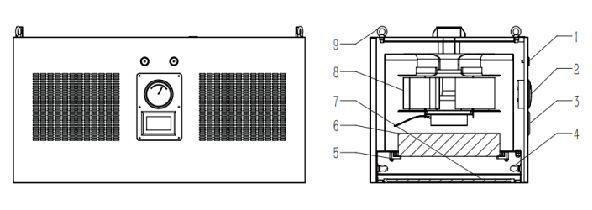 Structural diagram of laminar flow hood: 1. PAO detection port 2. Pressure difference meter 3. Controller 4. LED lighting 5. Pressing code 6. Liquid tank filter 7. Equalizing membrane 8. Fan 9. Lifting ring The working principle of the weighing hood: air is extracted from the clean room and sent inside after purification. The difference is that the weighing hood provides a negative pressure environment to protect the external environment from being polluted by the internal environment; laminar flow hoods generally provide a positive pressure Pressure environment, used to protect the internal environment from pollution. 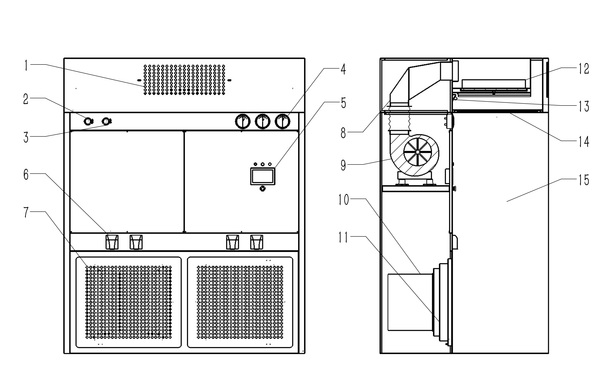 Structural diagram of negative pressure weighing room: 1. Top exhaust hole 2. PAO injection port 3. PAO sampling port 4. Filter differential pressure gauge 5. Control panel and operation buttons 6. Waterproof socket 7. Bottom return hole 8. Air duct 9. Fan 10. Bag-type medium-efficiency filter 11. Primary-efficiency filter 12. Liquid tank high-efficiency filter 13. Lighting and sterilizing lamps 14. Flow equalization membrane 15. Negative pressure working area 2. Applicable scenarios Due to the different design principles and operation methods of the two covers, the applicable scenarios are also different. Laminar flow hoods are usually suitable for laboratory operations such as chemical testing, food testing, and pharmaceuticals that need to protect operators and experimental materials. They can prevent dust, mold, bacteria, etc. from being brought into the operating area. The negative pressure weighing cover is more suitable for experimental operations involving radioactive elements, organic substances, etc. that need to avoid their release. 3. How to use The operation method of a laminar flow hood is usually to place the object to be operated on the work panel, and then put your hands into the hood to operate. The negative pressure weighing cover usually requires the items to be operated to be placed in a special weighing pan or mixer, and the operator observes the operating status from the side or top through a transparent material. 4. The difference between a weighing hood and a laminar flow hood Both laminar flow hoods and weighing hoods can create a local working environment with level 100 cleanliness and provide vertical one-way flow. Laminar flow hoods provide a positive pressure environment to protect the internal environment from contamination. They are usually used in combination and are more flexible. The air purification unit has no return air structure, and the supply fan takes air from the clean room; the weighing cover provides a negative pressure environment to prevent internal products from contaminating the outside world. It is an integral structure, fixedly installed, closed on three sides, in and out on one side, and purified Smaller range, usually used alone. |

 German
German French
French Italian
Italian Portuguese
Portuguese Japanese
Japanese Korrean
Korrean Russian
Russian




